ADB function
1. What is ADB
ADB (Android Debug Bridge) is a command-line tool used to communicate with Android devices. It is part of the Android SDK (Software Development Kit) and is primarily used for developing and debugging Android applications. ADB allows developers to interact with devices via the command line, executing various operations such as installing and uninstalling applications, copying files, running commands, and viewing logs.
You can download the ADB client here: https://developer.android.com/tools/releases/platform-tools
2. Setting Up ADB Connection IP Whitelist
ADB has extensive permissions, so for the security of your cloud phone, only the IP addresses configured in the whitelist are allowed to connect to ADB. Additionally, for security reasons, it is recommended to disable ADB on the cloud device when it is not in use.
You can configure the ADB connection IP whitelist for all cloud phones under your team settings:
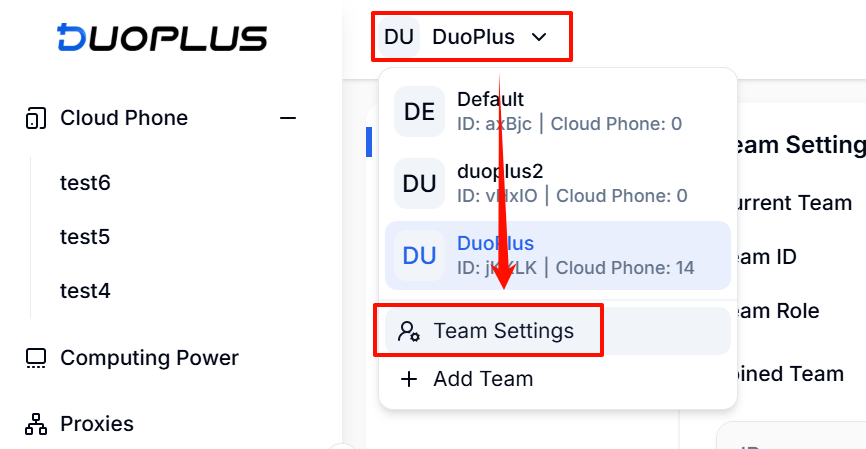
A maximum of 10 IP addresses can be configured in the whitelist. Once configured, you can enable ADB in the cloud phone list.
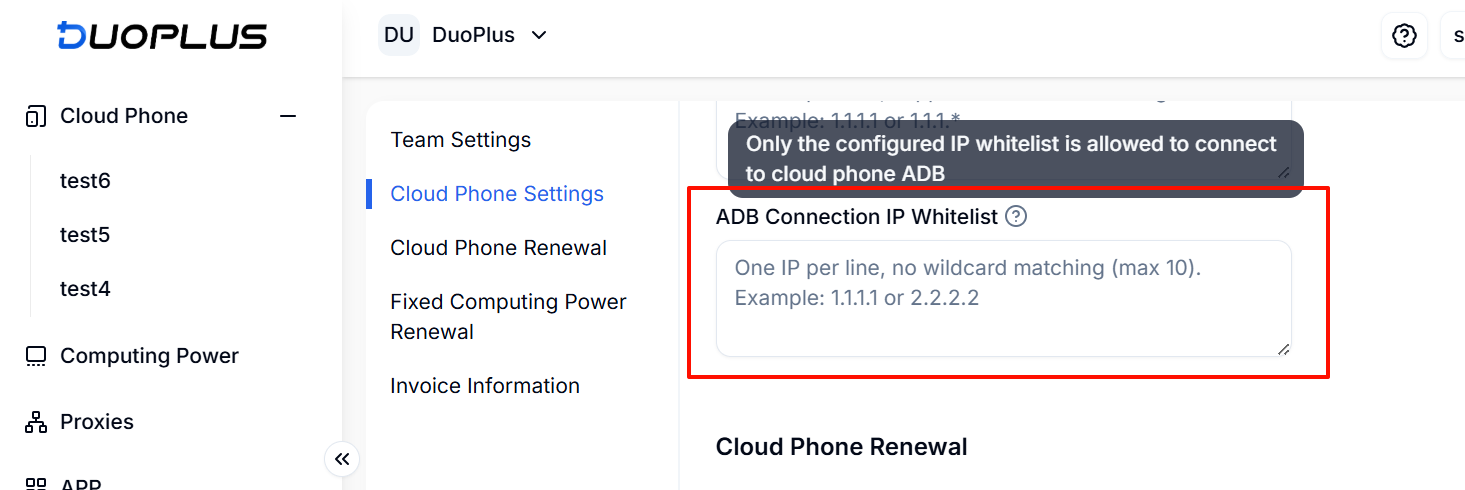
3. Enabling ADB
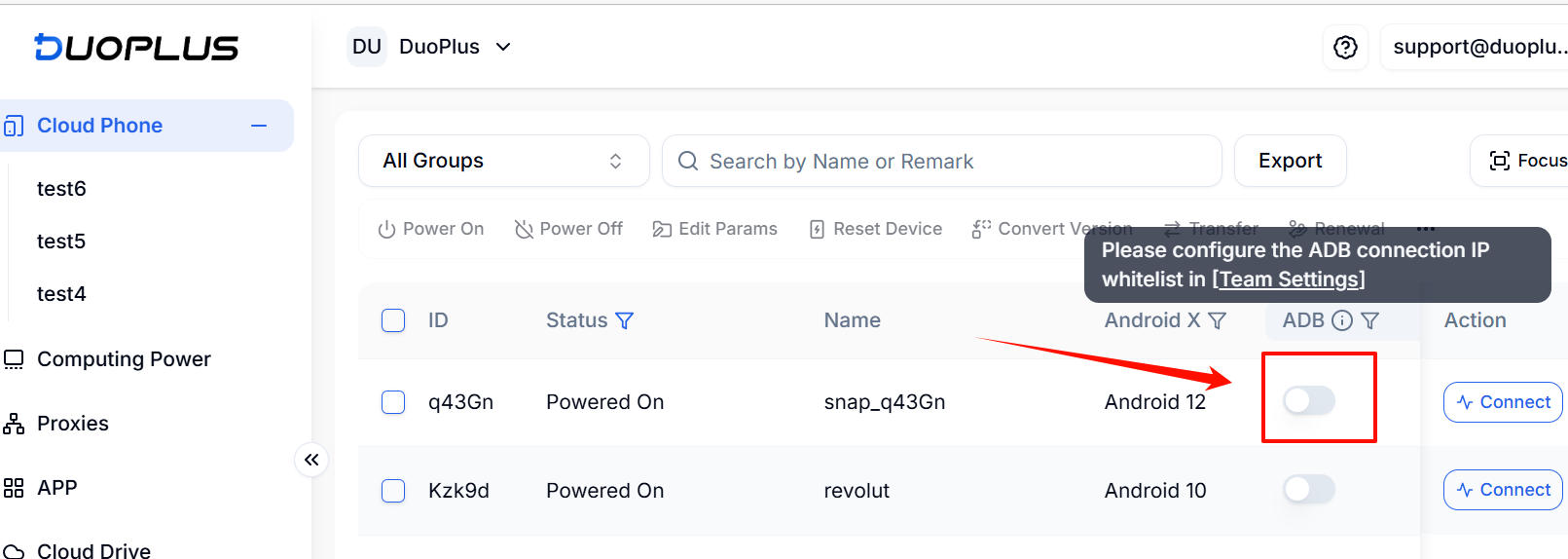
You can enable ADB for a single cloud phone directly from the list.
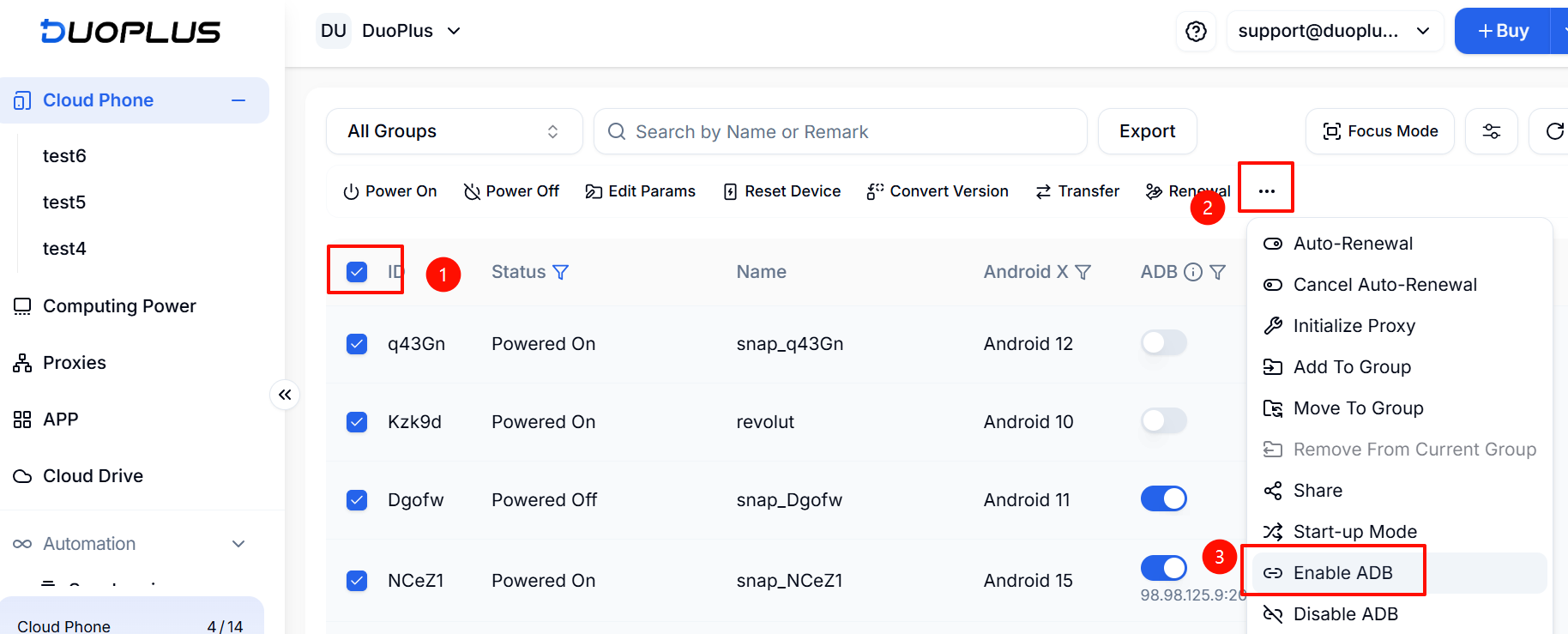
You can also enable ADB for multiple cloud phones in bulk.
4. Connecting to ADB
You need to first download the ADB client.
Windows users should use cmd; Mac and Linux users should use Terminal to enter the connection command copied from the DuoPlus Dashboard.
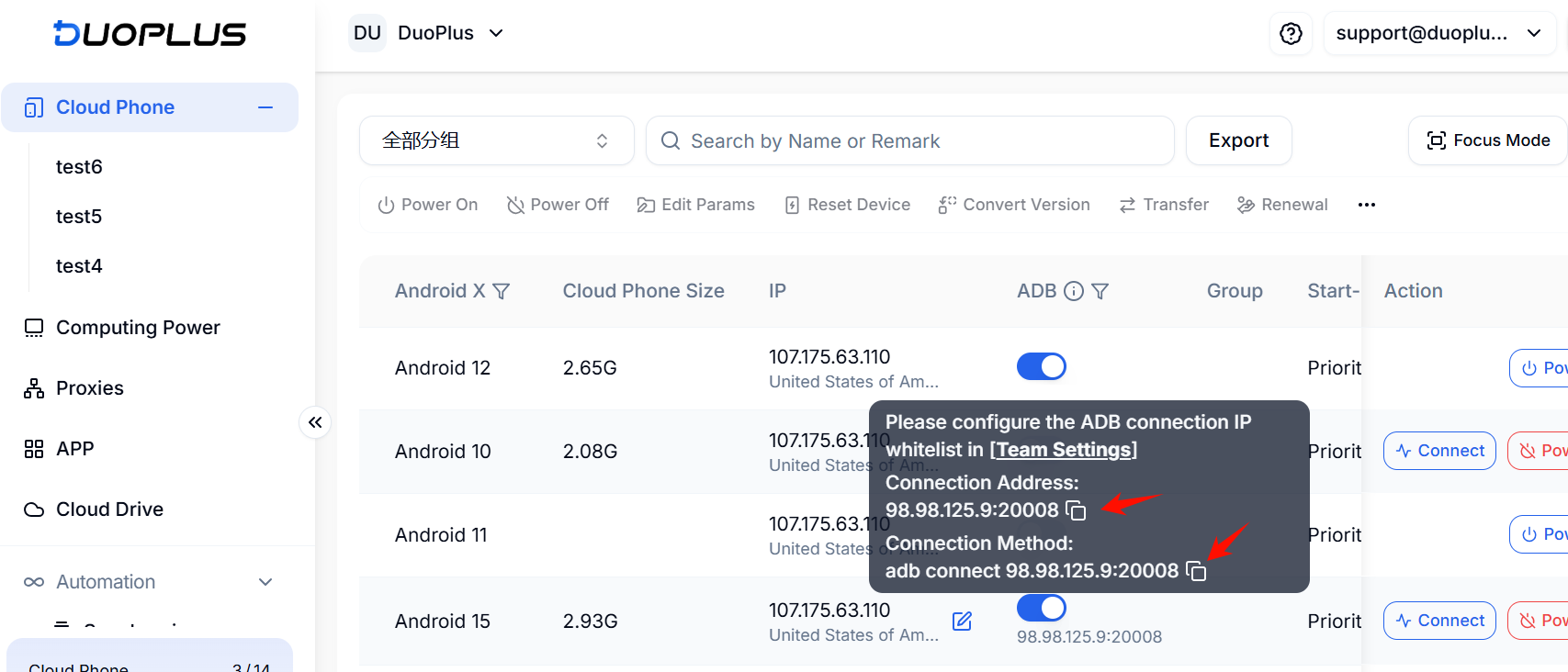
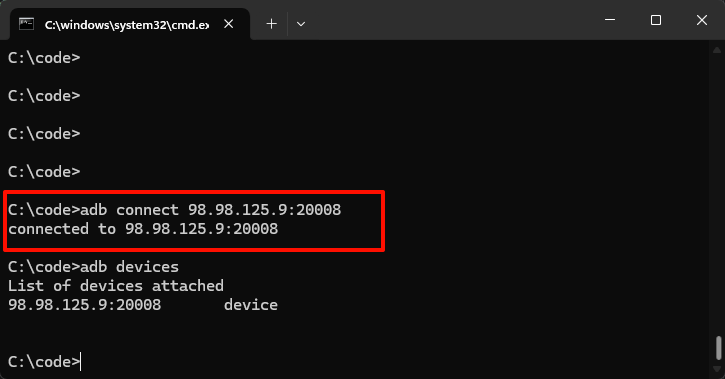
5. Common ADB Commands
Connect to ADB
adb connect [IP]:[port]Get ADB connected devices
adb devicesExecute a command
adb -s [IP]:[port] shell [command content]Push a file to the cloud device
adb -s [IP]:[port] shell push [local file path] [cloud device file path]
# Example for Windows
# adb -s [IP]:[port] shell push C:\User\DuoPlus\Desktop\abc.txt /sdcard/abc.txtClose the connection
adb disconnect [IP]:[port]For other common ADB commands, you can refer to the documentation: Common Commands
- Introduction
- Cloud Phone List
- Batch Power On
- Batch Power Off
- Batch Restart
- Cloud Phone Status
- Details
- Batch Modify Parameters
- Cloud Phone Model List
- Reset and Regenerate Device
- Batch Set Root
- Execute the ADB command
- Change sharing password
- Batch Enable ADB
- Batch Disable ADB
- Connected Member List
- Tag List
- Cloud Phone Resource List
- Resolution list
- Buy Cloud Phone
- Renew Cloud Phone
- How to develop plug-in modules
- How to Pass Google Verification
- Basic Functions
- Variables Overview
- Exception Handling
- Create Task Workflow
- DumpElement Tool Overview
- Page Operations
- Wait Operations
- Get Data
- Profile info
- Workflow Management
- Third-party tools
- Common Scenario 1: Custom Parameter Variable – Batch Text
- Common Scenario 2: Fetching Dynamic Parameters via Network Request
- Common Scenario 3: Retrieving Verification Codes from Email